Markets overview
Energy storage assets typically generate revenue in three ways; ancillary services, capacity market mechanisms and wholesale energy trading.
Grid operators depend on stabilisation assets like BESS to ensure the security of grids. These services encompass frequency regulation, voltage control, reserve services, and black start capabilities. These types of services are ancillary services and are merchant in nature.
Capacity markets are the preferred mechanism for grid operators to procure adequate generation capacity on the grid to meet the increasing electricity demand. Capacity market contracts are typically long-term contracts that represent long-term contracted income for the portfolio.
Energy storage systems can store electricity during troughs and discharge during peaks. This can often coincide with periods where renewable generation exceeds demand and is a form of merchant revenue in most markets (wholesale energy trading).
Merchant and Contracted Revenue Streams
The table below outlines GSF’s revenue streams across grids and primarily comprises merchant revenue streams (ancillary services and wholesale energy trading) given the current nature of the BESS revenue stack. Contracted revenue streams in the table below are designated with a ‘*’.Revenue streams for Battery Energy Storage Assets across GSF’s six markets
| Market | Market Structure | Revenue Streams | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| GB | National Grid | Capacity Market (CM)* | Procurement of future energy capacity to ensure sufficient generation on the system. |
| Firm Frequency Response (FFR) | Balancing supply and demand of electricity to ensure that frequency remains around 50Hz. | ||
| Dynamic Containment (DC) | Fast-acting post-fault service to contain frequency outside of acceptable limits. | ||
| Dynamic Moderation (DM) | Balancing supply and demand of electricity to ensure that frequency remains around 50Hz. | ||
| Dynamic Regulation (DR) | Balancing supply and demand of electricity to ensure that frequency remains around 50Hz on a faster timescale than DM. | ||
| Quick Reserve (QR) | Frequency management response responsible for restoring the energy imbalance and frequency of the grid for pre-fault disturbances. | ||
| Wholesale Trading | The trade of energy between generators and suppliers. | ||
| Triads | Top three half-hour peaks of national energy demand across the grid. | ||
| Ireland | EirGrid/SONI | Capacity Market (CM)* | Procurement of future energy capacity to ensure sufficient generation on the system |
| DS3 Programme (volume uncapped, volume capped) | • Volume uncapped: Procurement that does not limit the volume of the service being procured and to which regulated tariffs apply • Volume capped: Procurement where an upper limit is applied to the volume of relevant DS3 services being procured and for which prospective providers will offer a competitive price as part of their tender | ||
| Wholesale Trading | The trade of energy between generators and suppliers. | ||
| Germany | TSOs across 8 countries | Frequency Containment Reserve (FCR) | Primary ancillary service in Germany and serves to stabilise frequency deviations in the system. |
| Automatic Frequency Restoration Reserve (aFRR) | Secondary reserve service used to cover small imbalances in energy and power. | ||
| Wholesale Trading | The trade of energy between generators and suppliers. | ||
| Texas, US | ERCOT | Responsive Reserve Services (RRS) | Used to restore the frequency of the system within the first few minutes of an event that causes a significant deviation from the standard frequency. |
| ERCOT Contingency Reserve Service (ECRS) | A daily procured ancillary service introduced in June 2023 to respond to ramping of load or demand. | ||
| Wholesale Trading | The trade of energy between generators and suppliers. | ||
| Regulation Service Up and Regulation Service Down (Reg Up/Reg Down) | Continuously corrects minor frequency deviations pre-fault. | ||
| Non-Spinning Reserve Service | Provides additional dispatchable capacity when real-time reserves are low manually. | ||
| California, US | CAISO | Resource Adequacy (RA)* | Used to ensure stable and reliable capacity is available to the grid when needed by agreeing long-term contracts, able to provide c. 40% of revenues to a project, with capacity providers. |
| Wholesale Trading | The trade of energy between generators and suppliers. | ||
| Regulation Service Up and Regulation Service Down (Reg Up/Reg Down) | Continuously corrects minor frequency deviations pre-fault. | ||
| Non-Spinning Reserve Service | Provides additional dispatchable capacity when real-time reserves are low manually. This capacity will be ramped to a specific load requirement within 10 minutes. | ||
| Spinning Reserve Service | This service is provided by standby capacity from generation units already connected or synchronized to the grid and that can deliver their energy in 10 minutes when dispatched. |
RNS Announcements
-
Holding(s) in Company
23 June 2025 -
Strategy Update, Dividend, Unaudited NAV
18 June 2025 -
Holding(s) in Company
09 June 2025
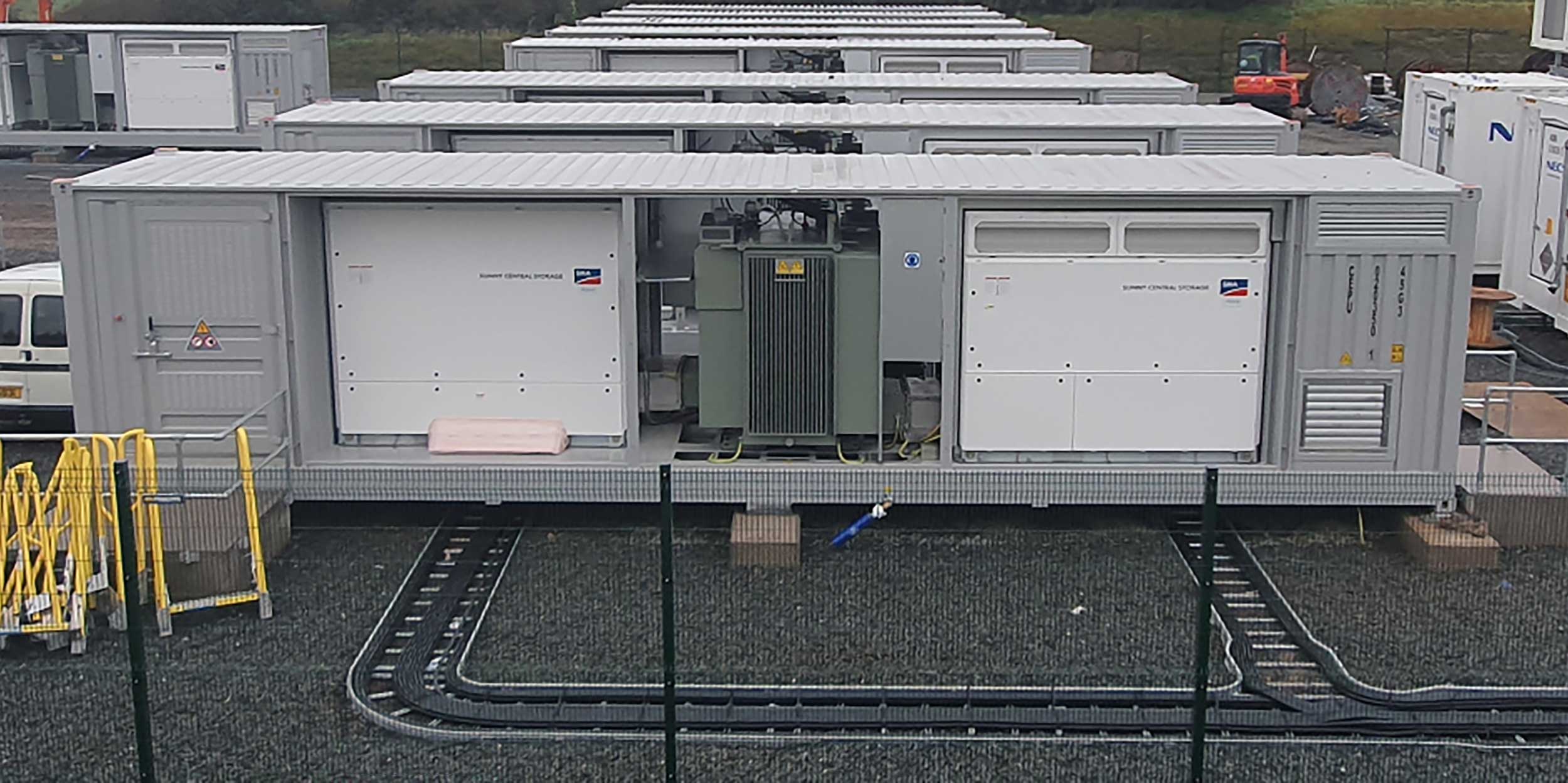
Our Portfolio
Find out about our portfolio
Investor Alert
Sign up for alerts